Class: Mammalia Order: Artiodactyla Family: Cervidae Genus: Cervus Species: elaphus
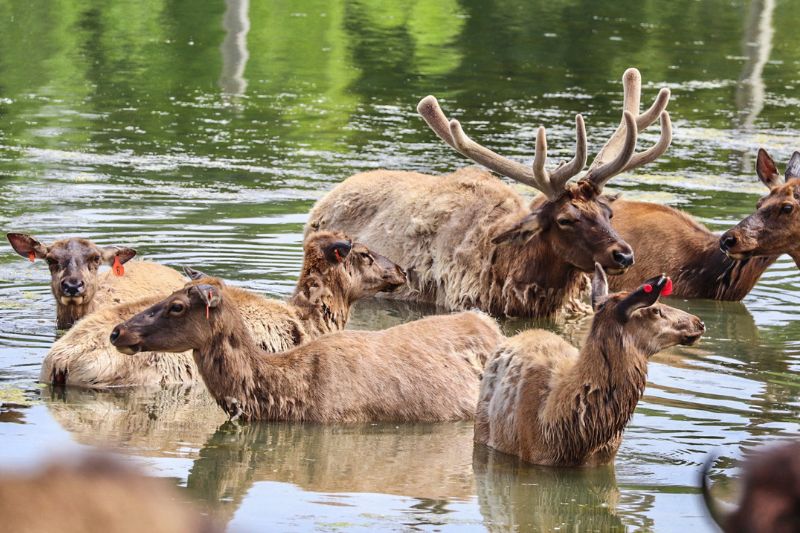
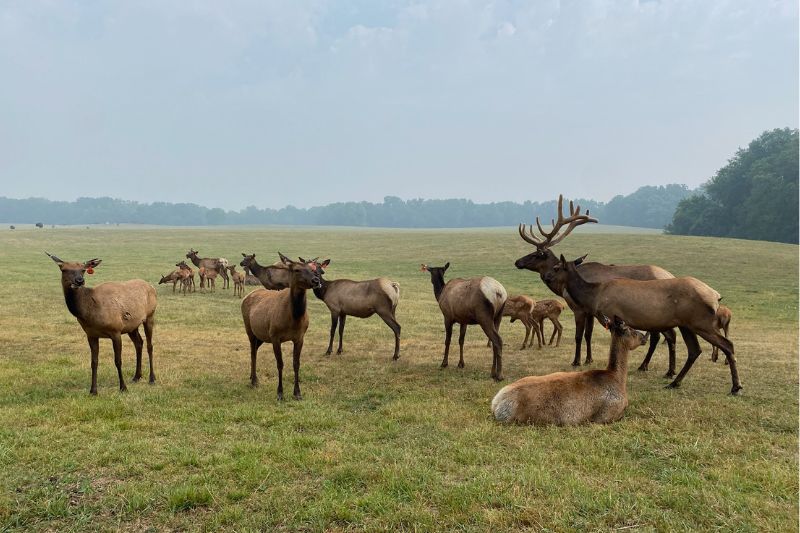
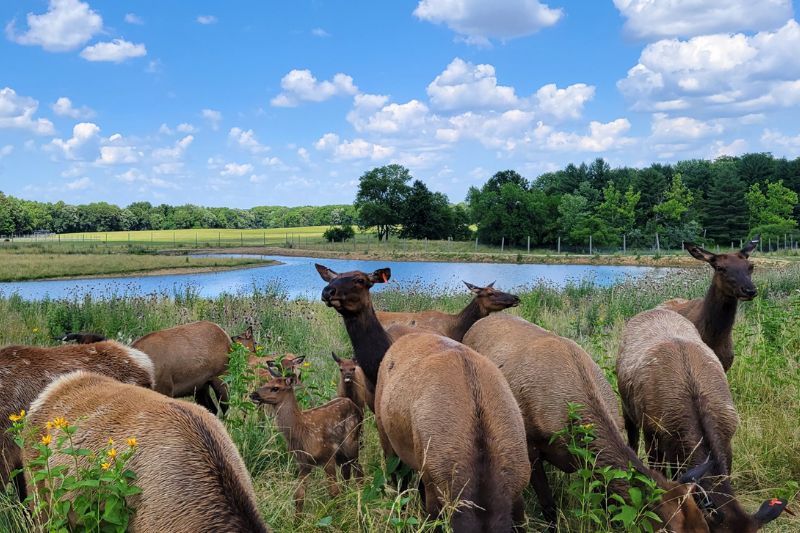
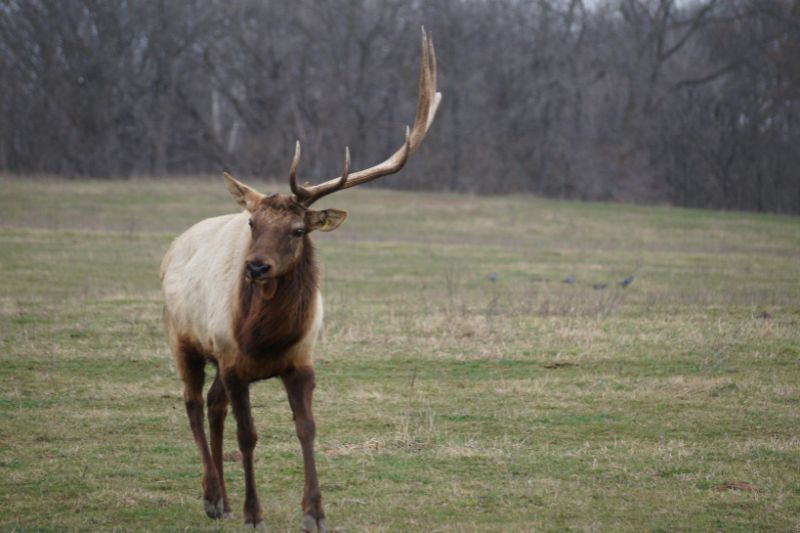
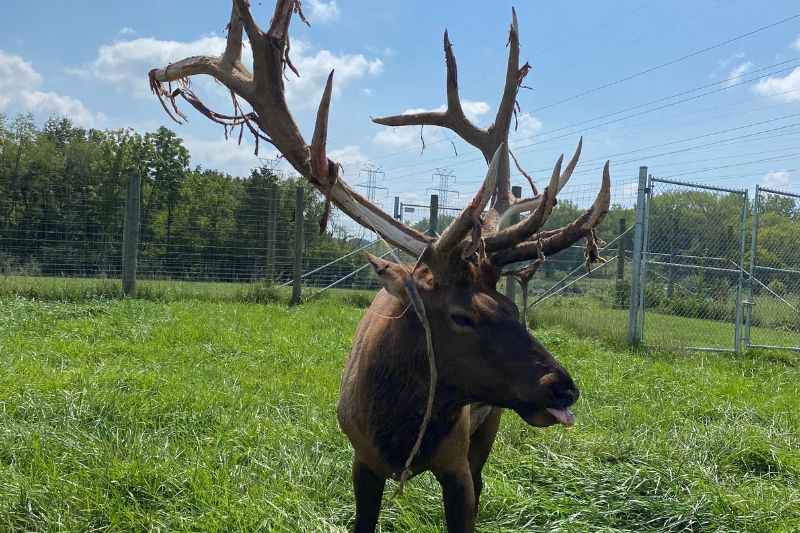
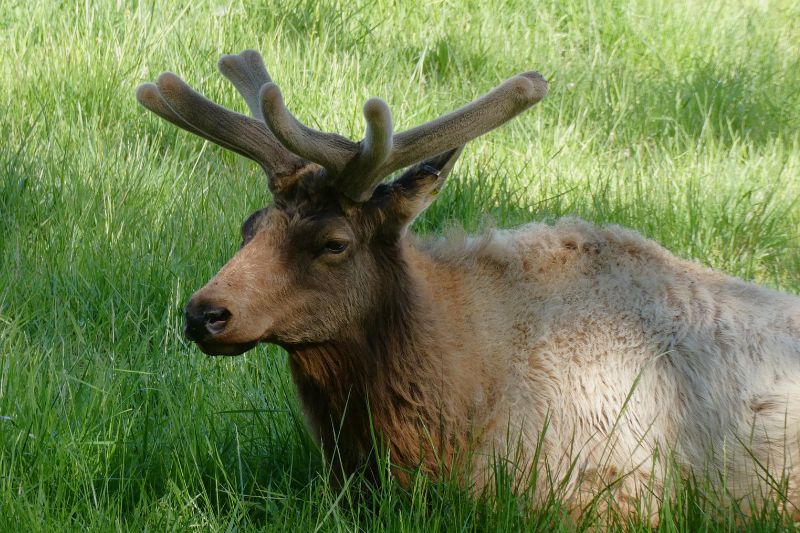
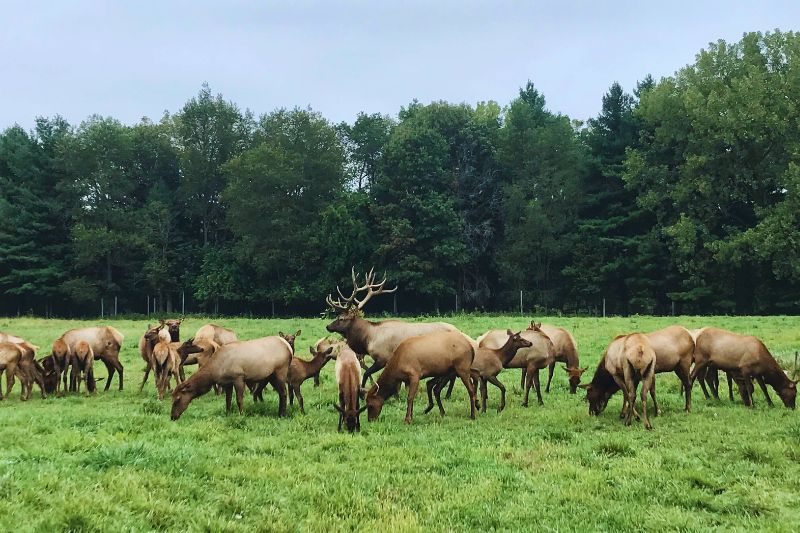
Elk are large social animals that herd together in mountain meadows and forests. Their most distinguishing features are their brown color, buff colored rump, and in the case of the males, or bulls, the massive, branching antlers.
These majestic animals are often referred to as both Elk and Wapiti (WAH-pih-tee). Wapati is a Shawnee Native American word meaning "white deer" or "light colored deer", an apparent reference to the animal's buff-colored rump.


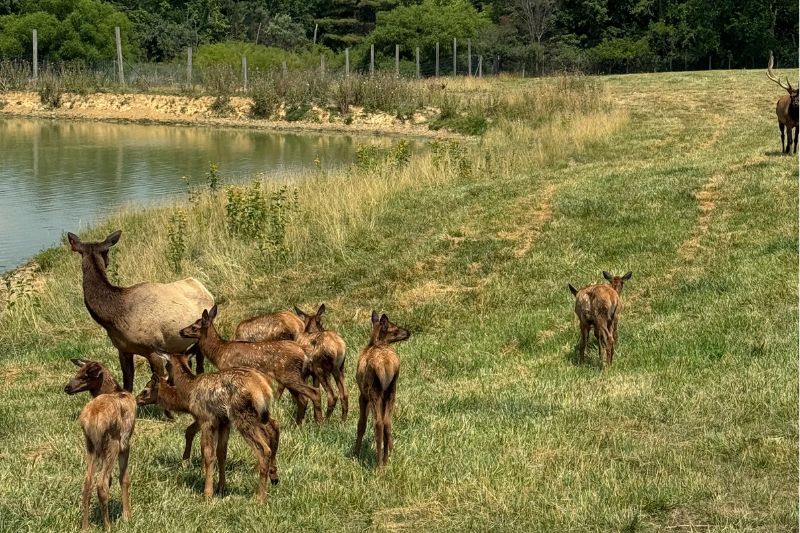
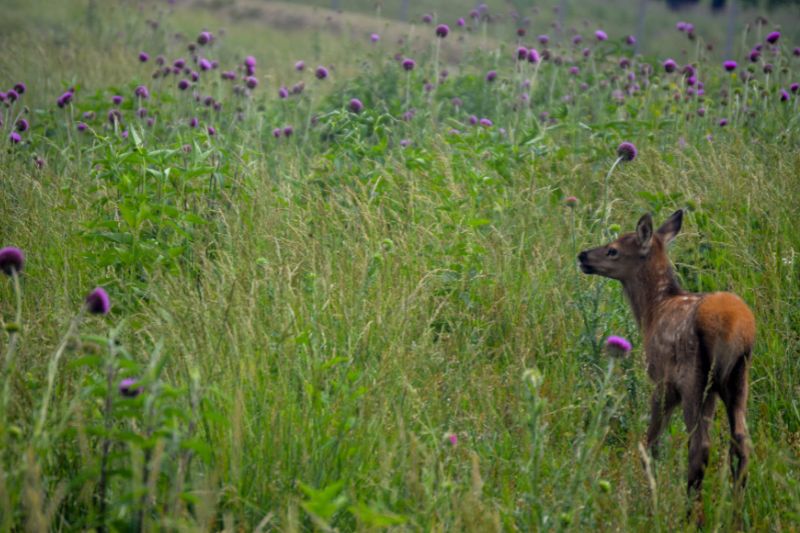
As summer begins, elk travel to higher elevations in search of fresh grazing areas. It’s in these mountain habitats that female elk give birth, usually to one calf. Remarkably, the newborn is able to stand on its feet within just 20 minutes of being born.
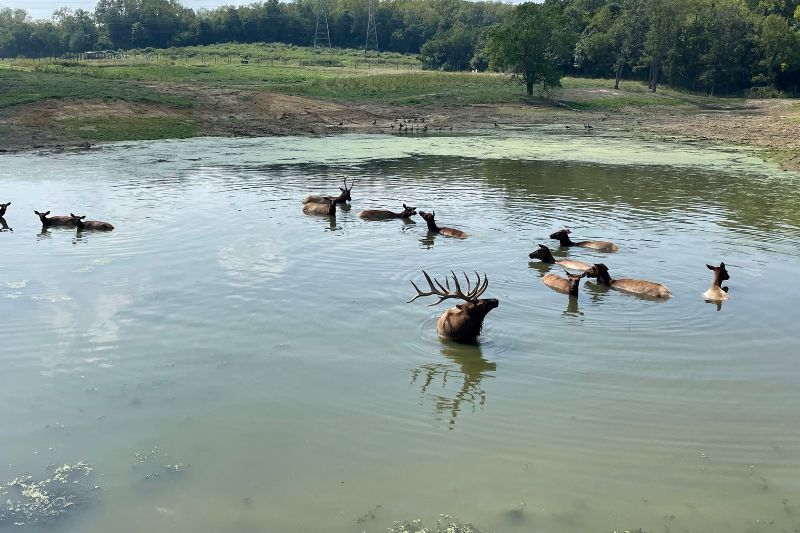
During winter, elk gather into larger groups, although males and females usually stay apart. These herds migrate to lower valleys, where they spend the season digging through snow to find grass or feeding on exposed shrubs.
Elk primarily eat grass, such as bluegrass, wheatgrass, bromegrass, and bunchgrass. They also consume flowering plants like clover, sticky geranium, fireweed, and alfalfa. In spring and summer, they feed on budding woody plants like aspen, cottonwood, and willow. By fall, they seek sugar-rich plants such as prairie sagewort. In winter, their diet shifts to dry grasses, bark, cattails, and other available vegetation.
Help Feed Our Elk
A bull elk’s antlers may reach 4 feet above its head so that the animal can be 9 feet tall. His antlers are an accessory to show his status. During the breeding, or "rutting" season, they are used to fend off other males to gather a harem of females to breed with. These antlers are shed in late winter every year, typically around February or March and start growing in the spring.
The distinct "bugle" of the large males also characterizes the rutting season. Conflict between competing males rarely turns violent; instead, a series of elaborate dances, mock fighting, bugling, and minor antler lockups determine dominance.
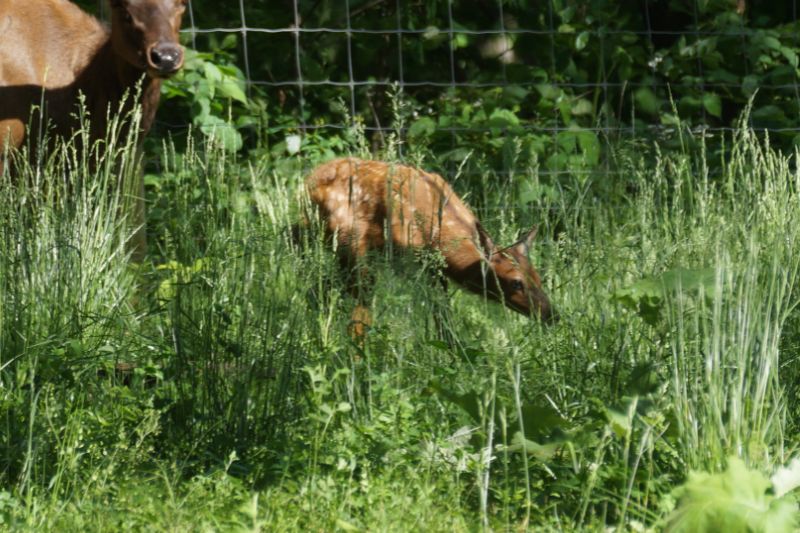
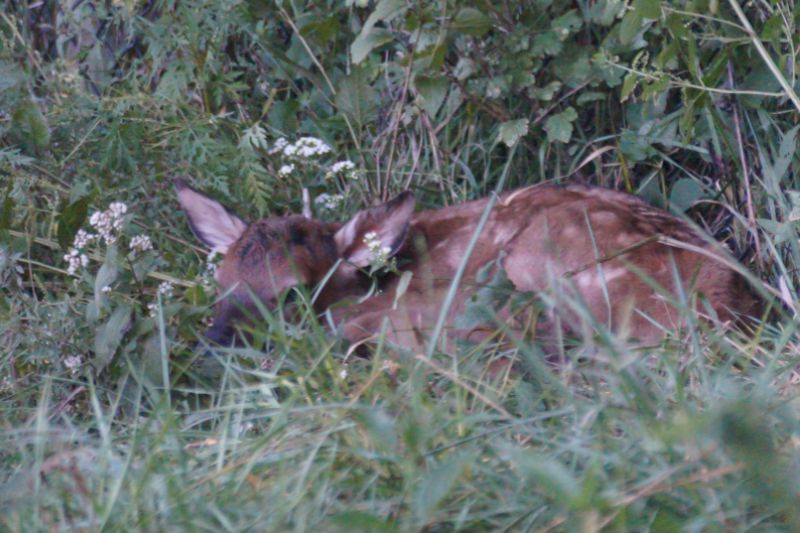
When born, baby elk, known as calves, weigh 30-40 lbs, have little or no scent, and have a natural camouflage to them. The mother will quickly hide the newborn in tall grass and brush while she feeds and draws predators away from her calf. Although the calves can stand and nurse about 30 minutes after birth, they can lay motionless and hide in one place for up to 15 days. During that time they nurse and can gain about 1 lb a day, staying safe from predators until it is ready to keep up with the herd.
Elk can live 10 to 12 years in the wild and can reach 22 years in captivity.














